Prepare Kubernetes
1. Import Images
1.1 Download and unzip the compressed files
Go to Requirement Page to download the latest install packages.
1.2 Loading images
1.2.1 Older Kubernetes Versions
If your kubernetes version is older then v1.24, and you use docker to manage your images, enter the command below
docker load -i <image_name>
1.2.2 Different Container Engines
If your kubernetes is v1.24 or newer, docker load command is deprecated
, find out the version of your control-plane by entering the following command
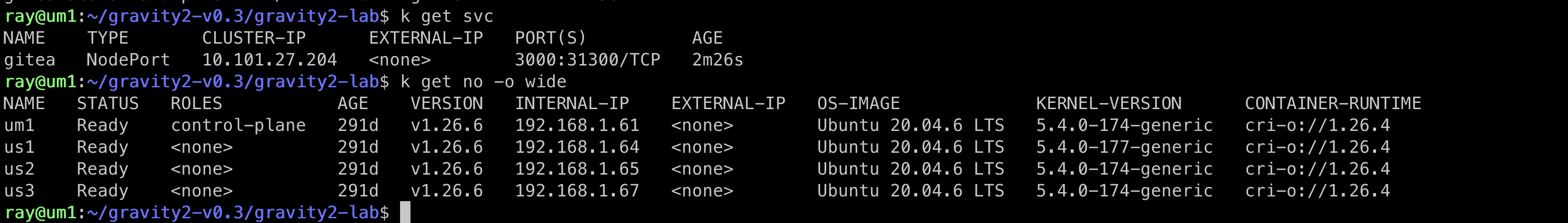
kubectl get node -o wide
If your container engine is crio
sudo podman load <image>
If your container engine is containerd
ctr -n k8s.io image import <image>
2. Configure Gravity Environment
2.1 Create Namespace
If namespace is set as bbg-gravity all the .yaml files pertaining the same gravity cluster should have the same namespace configured in the .yaml files
⚠️ Caution: Any
.yamlfile names may vary accordingly. Please verify whether your.yamlfiles match its acutal names.
Enter the command below
kubectl apply -f 01-bbg-namespace.yaml
Alternatively, create our own namespace
kubectl create ns <namespace_name>
2.2 Set-up Gitea
Gitea is a lightweight version control repository. In this example we use gitea to store atomic files.
2.2.1 Deploy
Enter the command below
kubectl apply -f 02-bbg-gitea.yaml
2.2.2 Verify
Verify whether the pod was successfuly created
kubectl -n bbg-gravity get pods
Verify whether the service is up
kubectl -n bbg-gravity get svc
Acquire the node-port Cluster-IP
Open a browser and connect to the node-port IP (i.e., http://192.168.100.154:31300)/)
Once nodeport is configured, it is accessible on any kubernetes node which means you can connect to the above ip
http://192.168.1.61:31300orhttp://192.168.1.61:31300If you are setting up gitea for the first time, you may need to complete the initial setup and enter the generated token in
gitea-token.txt